Do LED light bulbs get hot? Yes, LED light bulbs do get warm, but they typically generate significantly less heat than traditional incandescent bulbs. This heat is primarily a byproduct of their operation and is managed through various design strategies.
For decades, we’ve relied on incandescent bulbs to light our homes. These bulbs worked by heating a filament until it glowed, producing light. This process was notoriously inefficient, with most of the energy turning into heat rather than light. When LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) arrived, they promised a cooler, more energy-efficient alternative. But how hot do they actually get? This guide will explore LED bulb temperature, LED heat output, and the factors influencing LED light heat.
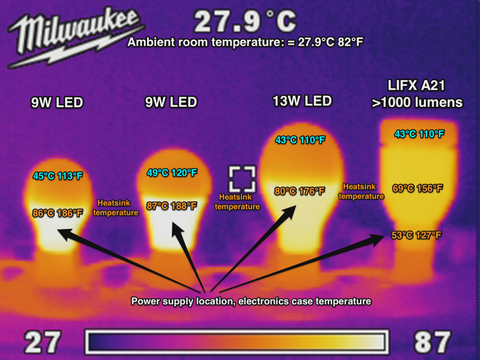
Image Source: cdn.shopify.com
The Science Behind LED Heat
LEDs are semiconductor devices. When electricity flows through them, electrons release energy in the form of photons, which we see as light. This process is much more efficient than incandescence. However, some energy is still lost as heat. The LED bulb temperature is a crucial factor in its lifespan and performance. If an LED gets too hot, its efficiency drops, and its lifespan can be drastically shortened. This is why effective LED bulb thermal management is so important in their design.
Where Does the Heat Come From?
The primary source of heat in an LED bulb is the semiconductor junction itself. This is where the magic of light emission happens. However, not all heat is generated directly by the light-producing elements. Other components within the bulb, such as the driver electronics that convert AC power to the DC power LEDs need, also contribute to LED heat generation.
Why is Heat Important?
The LED light heat generated needs to be managed effectively. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which radiate most of their heat away as infrared radiation (which we feel as heat), LEDs produce heat primarily at the back of the bulb, where the heat sinks are located. This localized heat can damage the sensitive electronic components if not properly dissipated. Understanding the LED bulb operating temperature is key to ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
Factors Affecting LED Bulb Temperature
Several factors influence how hot an LED bulb gets. These include the bulb’s design, the quality of its components, and the environment in which it’s used.
Bulb Design and Construction
The physical structure of an LED bulb plays a significant role in its LED bulb heat dissipation.
- Heat Sinks: Most LED bulbs feature a heat sink, typically made of aluminum or a similar metal. This is a critical component designed to draw heat away from the LED chip and dissipate it into the surrounding air. The larger and more efficient the heat sink, the better the LED light bulb thermal performance.
- Materials Used: The materials used in the bulb’s construction, from the housing to the internal wiring, affect heat transfer.
- Driver Electronics: The efficiency and design of the driver circuit can impact the overall LED heat output. A poorly designed driver can generate more heat.
LED Chip Quality and Efficiency
The LED light temperature rating is also influenced by the quality of the LED chips themselves.
- Efficiency: More efficient LED chips convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into light, generating less waste heat.
- Power Output: Higher wattage LEDs will naturally generate more heat than lower wattage ones.
- Manufacturer Quality: Reputable manufacturers invest in better quality LEDs and thermal management systems, leading to lower operating temperatures and longer lifespans.
Environmental Conditions
The ambient temperature and ventilation in the room where the LED bulb is installed significantly impact its operating temperature.
- Ambient Temperature: A hotter room will mean the LED bulb has to work harder to dissipate its heat, leading to a higher internal temperature.
- Ventilation: Enclosed fixtures or poor ventilation can trap heat around the LED bulb, preventing effective LED bulb heat dissipation and increasing its LED bulb operating temperature.
- Fixture Type: Some light fixtures are designed to be more open, allowing for better airflow, while others are enclosed and can trap heat.
Measuring LED Bulb Temperature
How can you tell how hot an LED bulb is getting? While you can’t usually touch them directly without risk of burns (especially immediately after being on), there are ways to get an idea of their LED bulb temperature.
Infrared Thermometers
These handheld devices can measure the surface temperature of objects without contact. They are excellent for checking the temperature of the heat sink or the exterior of the bulb.
Thermal Imaging Cameras
For a more detailed analysis, thermal imaging cameras can visualize the heat distribution across the bulb and its surroundings, offering insights into the effectiveness of the LED bulb thermal management.
Bulb Specifications
Manufacturers usually provide specifications for their LED bulbs, including their LED bulb temperature limits and expected operating temperatures. Always check the product packaging or manufacturer’s website for this information.
Typical LED Bulb Temperatures
So, what are we talking about in terms of actual numbers? The LED bulb temperature can vary, but generally, they operate much cooler than older technologies.
Comparison with Incandescent and Halogen Bulbs
- Incandescent Bulbs: The glass surface of an incandescent bulb can reach temperatures of 200-250°C (392-482°F). The filament itself gets much hotter, around 2700°C (4892°F).
- Halogen Bulbs: These are slightly more efficient than standard incandescents but still get very hot, with surface temperatures often between 100-150°C (212-302°F).
- LED Bulbs: The surface temperature of an LED bulb typically ranges from 40-70°C (104-158°F). The hottest part is usually the base where the LED chip and driver are located, and this is where the heat sink is most crucial.
What About Different Types of LEDs?
The type of LED bulb can also influence its temperature.
- Standard A19 Bulbs: These common household bulbs are designed for general lighting and usually operate within the typical range.
- High-Power Spotlights or Floodlights: These bulbs often require more robust LED bulb thermal management due to their higher wattage and concentrated light output. They might operate at the higher end of the temperature scale or require more sophisticated cooling mechanisms.
- Specialty LEDs (e.g., for grow lights, automotive): These can have different LED bulb temperature limits depending on their specific application and power requirements.
The Impact of Heat on LED Performance
LED light heat is not just an inconvenience; it directly affects how well the bulb works and how long it lasts.
Lifespan Reduction
The most significant impact of excessive heat on an LED is a reduced lifespan. For every 10°C increase in LED bulb operating temperature, the lifespan of an LED can be reduced by half. This is a crucial aspect of LED bulb thermal performance.
Lumen Depreciation
Heat also causes lumen depreciation, which is the gradual decrease in light output over time. An LED that runs too hot will dim faster than one that is kept cool.
Color Shift
In some cases, excessive heat can also cause a shift in the LED’s color temperature, meaning the light might appear warmer or cooler than intended.
Ensuring Proper LED Bulb Heat Dissipation
Good LED bulb heat dissipation is paramount for maximizing the lifespan and performance of your LED bulbs. Here’s how it’s achieved and what you can do.
Internal Mechanisms
Manufacturers employ several internal strategies for LED bulb thermal management:
- Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs): These materials, such as thermal paste or pads, are placed between the LED chip and the heat sink to ensure efficient heat transfer.
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): The LEDs are mounted on PCBs that are designed to conduct heat away from the chips. Metal-core PCBs are often used for better thermal conductivity.
- Internal Airflow: Some designs incorporate small air channels within the bulb to promote passive airflow, aiding heat dissipation.
External Factors You Control
You can also influence LED bulb heat dissipation through your choices:
- Choosing the Right Fixture: Opt for fixtures that allow for good airflow around the bulb. Avoid fully enclosed fixtures unless the LED bulb is specifically rated for them.
- Ventilation: Ensure the area where you install LED bulbs has adequate ventilation.
- Choosing Quality Bulbs: Invest in bulbs from reputable brands that have a proven track record of good LED light bulb thermal performance. They will have invested in better LED bulb heat generation control.
- Dimmer Compatibility: Ensure your dimmer switch is compatible with LED bulbs. Using an incompatible dimmer can cause the LED to flicker, overheat, and shorten its lifespan.
Understanding LED Bulb Temperature Limits
Every electronic component has LED bulb temperature limits. Exceeding these limits can lead to immediate failure or gradual degradation.
Junction Temperature
The most critical temperature to consider is the LED junction temperature. This is the temperature of the semiconductor material where light is generated. Manufacturers specify a maximum junction temperature, often around 125°C (257°F) for typical LEDs, though specialized LEDs might have different limits. However, it’s crucial to keep the LED bulb operating temperature well below this limit for optimal performance and longevity.
Case Temperature
This refers to the temperature of the LED package or the housing of the LED chip. It’s usually lower than the junction temperature but still an important indicator of LED heat output.
Ambient Temperature Ratings
Bulbs are often rated for a maximum ambient operating temperature. For instance, a bulb might be rated for operation in ambient temperatures up to 40°C (104°F). Using it in a hotter environment will affect its LED bulb temperature.
Deciphering LED Light Temperature Ratings
The LED light temperature rating refers to the temperature at which the bulb is designed to operate reliably. This is distinct from the color temperature of the light (measured in Kelvin).
- Operating Temperature Range: Manufacturers will specify an ideal operating temperature range. For example, -20°C to +40°C (-4°F to +104°F).
- Storage Temperature: This is the temperature range in which the bulb can be stored without damage.
Common Misconceptions About LED Heat
There are a few common misunderstandings when it comes to LED heat.
“LEDs Don’t Get Hot At All”
This is incorrect. While LEDs are much cooler than incandescents, they do generate heat. The key is effective LED bulb thermal management and LED bulb heat dissipation.
“The Bulb Feels Cool, So It’s Fine”
The exterior of an LED bulb might feel only slightly warm, but the internal components, particularly the LED chips and driver, could be running at a higher temperature. The effectiveness of the heat sink is crucial here for managing the LED heat output.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I use an LED bulb in a fully enclosed light fixture?
It depends on the specific LED bulb. Many standard LED bulbs are not designed for fully enclosed fixtures because they trap heat, reducing LED bulb heat dissipation and potentially shortening the bulb’s lifespan. Look for LED bulbs specifically rated as “enclosed fixture rated” or “air-tight fixture compatible.” These bulbs have improved LED bulb thermal management to handle the confined heat.
Will an LED bulb get hot enough to cause a fire?
It is highly unlikely for a properly manufactured and installed LED bulb to cause a fire. Reputable manufacturers design their bulbs to operate within safe temperature limits, and they incorporate safety features to prevent overheating. The primary risk of overheating is damage to the bulb itself, not a fire hazard. However, using damaged or faulty bulbs, or bulbs that have been significantly modified, could pose a risk. Always adhere to the LED bulb temperature limits.
How can I tell if my LED bulb is overheating?
Signs of an overheating LED bulb can include:
- The bulb housing becoming excessively hot to the touch (use caution).
- Flickering or dimming of the light.
- Unusual smells or discoloration of the bulb.
- The bulb shutting off intermittently as a protective measure.
If you notice any of these, it’s a sign of poor LED bulb thermal performance or an issue with the fixture or installation, impacting the LED heat output.
Does the color of the LED bulb affect how hot it gets?
The color temperature of the light (e.g., warm white, cool white) is determined by the phosphors used in the LED package and has a minimal direct impact on LED bulb temperature. However, the overall efficiency of the LED package, which can be influenced by the technology used to produce different colors, will affect LED heat generation. For example, some high-CRI (Color Rendering Index) LEDs might be slightly less efficient and produce a bit more heat.
What is the warranty period for LED bulbs, and does heat affect it?
LED bulb warranties typically range from 2 to 10 years, depending on the manufacturer and the bulb’s intended use. Overheating due to poor LED bulb thermal management or installation can void the warranty, as it falls outside the intended operating conditions and degrades the LED light bulb thermal performance.
How does the wattage of an LED bulb relate to its heat output?
Higher wattage LED bulbs consume more power and therefore will generally produce more heat. However, the LED heat output is also directly related to the efficiency of the bulb. A high-efficiency, high-wattage LED might still produce less heat per lumen than a lower-wattage, less efficient LED. Always consider the overall LED bulb heat generation and how it’s managed.
What is the difference between LED heat output and LED light heat?
These terms are often used interchangeably and refer to the thermal energy generated by the LED bulb during operation. LED heat output refers to the amount of heat the bulb emits, while LED light heat can describe the heat that is a byproduct of the light-producing process. Both point to the necessity of effective LED bulb thermal management.
What are the typical LED bulb temperature limits for indoor lighting?
For most common indoor LED bulbs (like A19, GU10), the external casing temperature should ideally stay below 70°C (158°F). The internal components, particularly the LED junction, will be hotter, but the external temperature gives a good indication of overall heat management. It’s crucial to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the precise LED bulb temperature limits.
How does an LED bulb’s thermal performance affect its energy efficiency?
As an LED bulb heats up, its efficiency can decrease. This means it might convert less electricity into light and more into heat. Effective LED bulb heat dissipation keeps the LED chip at a lower LED bulb operating temperature, thus maintaining its energy efficiency and contributing to its overall LED bulb thermal performance. Poor LED bulb thermal management can lead to a less efficient and hotter bulb.
