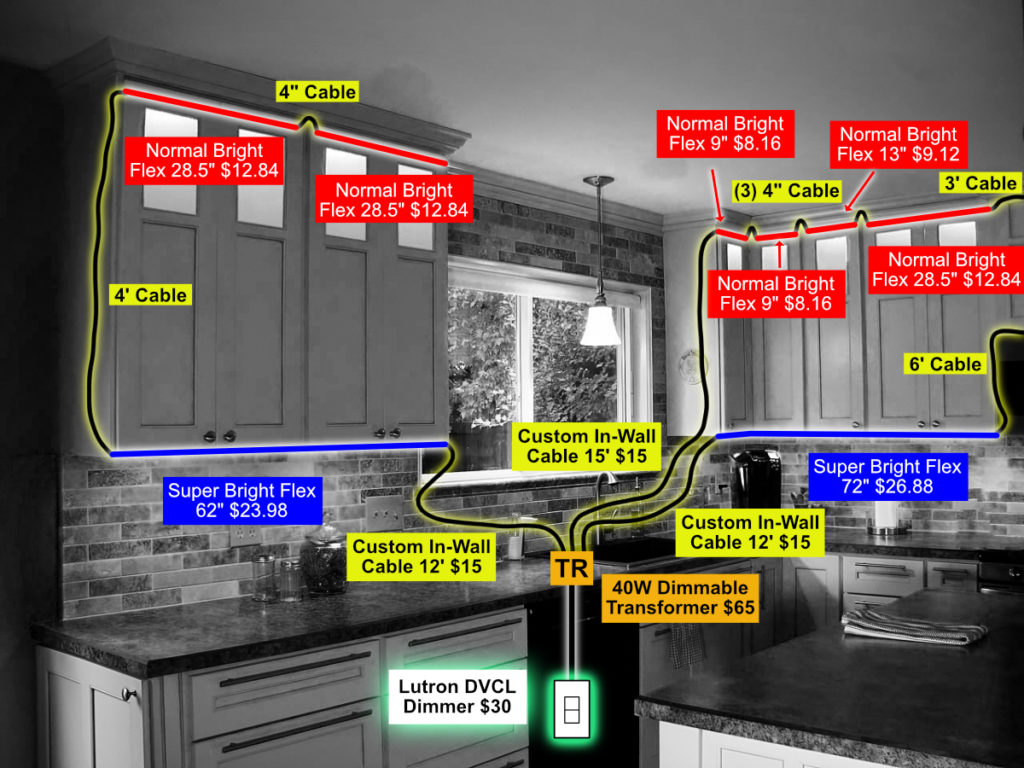
Image Source: www.inspiredled.com
How To Hardwire LED Light Strips: Step-by-Step
Can you connect LED light strips directly to mains power? Yes, with the right setup and safety precautions, you can hardwire LED light strips for a clean, permanent installation. This process involves connecting your low voltage LED wiring directly to a suitable power source, often bypassing the standard plug-in adapter. Direct wiring LED lights ensures a more integrated and aesthetically pleasing look, especially for custom lighting projects or permanent fixtures. This guide will walk you through how to hardwire LED light strips, covering everything from choosing the right components to safely making the connections. We’ll delve into LED strip wiring, connecting LED strips to mains power, and the crucial steps for permanent LED strip installation.
Deciphering LED Strip Power Requirements
Before you even think about touching wires, it’s vital to fathom your LED light strips’ power needs. Not all LED strips are created equal. They operate on different voltage levels, and understanding this is the cornerstone of a successful and safe installation.
Voltage Specifics
Most LED strips are either 12-volt DC or 24-volt DC. Some specialized strips might use 5-volt DC. It’s crucial to identify the exact voltage rating of your specific LED strip. This information is usually printed on the strip itself, its packaging, or the product’s specifications sheet.
- 12V DC LED Strips: These are very common for accent lighting, under-cabinet lighting, and various DIY projects. They require a power supply that outputs 12 volts of direct current.
- 24V DC LED Strips: These are gaining popularity for longer runs and higher-power applications. They offer better efficiency over longer distances compared to 12V strips. They need a 24-volt DC power supply.
- 5V DC LED Strips: Often found in smaller, more decorative applications or for integration with microcontrollers like Arduino. They require a 5-volt DC power supply.
Wattage Matters
Beyond voltage, you need to know the wattage of your LED strip. This tells you how much power the strip consumes. It’s usually measured in watts per meter (W/m) or watts per foot (W/ft).
- Calculating Total Wattage: To determine the total wattage required, multiply the strip’s wattage per unit length by the total length of the strip you’ll be using. For example, if you have a 5-meter strip that consumes 10W per meter, your total wattage is 5 meters * 10 W/m = 50 watts.
This total wattage is critical for selecting the correct LED power supply connection and ensuring it can handle the load without overheating.
Choosing the Right LED Power Supply
When wiring LED strips without a plug, the power supply unit (PSU) is your hero. It converts the mains AC power (like what comes out of your wall socket) into the low DC voltage that your LED strips need. This is often referred to as an LED strip transformer connection or simply an LED power supply connection.
Types of Power Supplies for Hardwiring
For permanent LED strip installation, you’ll typically use one of two types of power supplies:
- Switch-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS): These are the most common and efficient. They are compact and convert AC to DC effectively. When hardwiring, you’ll look for an SMPS that has screw terminals for direct wire connections rather than a plug.
- LED Drivers: These are specialized power supplies designed specifically for LEDs. They often offer features like dimming capabilities and constant current or constant voltage output, depending on the LED strip’s design. For most LED strips, you’ll use a constant voltage driver.
Key Factors for Power Supply Selection
When selecting a power supply for direct wiring LED lights, consider these points:
- Voltage Output: Must match your LED strip’s voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V DC).
- Wattage Capacity: The PSU’s wattage rating must be at least 20% higher than the total wattage of your LED strips. This provides a safety margin and prevents the PSU from running at its maximum capacity, which can shorten its lifespan. So, if your strips need 50 watts, get a PSU rated for at least 60 watts (50 * 1.20 = 60).
- Amperage Output: Amperage (measured in amps, A) is also important. Wattage = Voltage * Amperage. Ensure the PSU’s amperage output is sufficient for your strips. If your strips need 50W at 12V, that’s 50W / 12V = 4.17A. You’d need a 12V PSU that provides at least 4.17A, preferably more (e.g., 5A or 6A).
- Enclosure Type: For hardwiring, you’ll want a PSU with an enclosed metal or plastic casing and accessible screw terminals. Some are designed for mounting inside junction boxes or directly onto surfaces.
- IP Rating: If the installation is in a damp or outdoor environment, choose a PSU with an appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) rating to protect it from moisture and dust.
Table 1: Power Supply Selection Guide
| LED Strip Wattage (Total) | Required PSU Wattage (Min.) | Required PSU Amperage (Min. at 12V) | Required PSU Amperage (Min. at 24V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20W | 24W | 2A | 1A |
| 40W | 48W | 4A | 2A |
| 60W | 72W | 6A | 3A |
| 80W | 96W | 8A | 4A |
| 100W | 120W | 10A | 5A |
Note: Always add a 20% buffer to your total LED strip wattage to find the minimum required PSU wattage.
Essential Tools and Materials for Hardwiring
Having the right tools makes the job smoother and safer. Here’s what you’ll likely need for connecting LED strips to mains power:
- LED Light Strips: Ensure you have the correct voltage and wattage.
- DC Power Supply (PSU): Matched to your LED strip’s voltage and with sufficient wattage.
- Wire Strippers: For removing insulation from wires.
- Wire Cutters: For cleanly cutting wires.
- Screwdriver Set: To open PSU enclosures and secure wire connections.
- Electrical Tape: For insulating connections.
- Wire Connectors: Such as Wago connectors or screw terminals, for secure wire joining.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: For insulating and protecting soldered or crimped connections.
- Soldering Iron and Solder (Optional but Recommended): For making very secure and robust connections.
- Multimeter: Essential for testing voltage and continuity to ensure correct connections.
- Wire: Appropriate gauge wire for the current. Check the PSU and LED strip specifications. Typically, 18-gauge or 16-gauge wire is suitable for most low-voltage applications.
- Cable Management Tools: Zip ties, cable clips, or conduit to neatly route wires.
- Drill and Drill Bits: If you need to pass wires through walls or mounting surfaces.
- Safety Glasses: Always protect your eyes.
The Step-by-Step Process of Hardwiring LED Strips
Now, let’s get to the core of how to hardwire LED light strips. This involves careful preparation and precise connections. Remember, when working with mains voltage, safety is paramount. If you are not comfortable with electrical work, hire a qualified electrician.
Step 1: Safety First – Disconnect Power
Before you begin any work, ensure the power to the circuit you’ll be using is completely turned OFF at the breaker box. Double-check with a non-contact voltage tester to confirm the power is indeed off. This is a non-negotiable step for permanent LED strip installation.
Step 2: Prepare the LED Strip
Most LED strips have connection points marked with “+” and “-“. You’ll need to expose these connection points.
- Cutting the Strip: If your strip is longer than needed, cut it only at the designated cutting marks (usually indicated by scissors icons or copper pads).
- Exposing Wires: For LED strip wiring, you’ll typically need to solder wires to the copper pads on the strip.
- Gently use wire strippers or a craft knife to remove a small section of the protective silicone coating over the copper pads, if present. Be careful not to damage the copper itself.
- If you’re soldering, tin the copper pads on the strip (apply a thin layer of solder) and tin the ends of the wires you’ll be using.
Step 3: Prepare the Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Your chosen power supply will have input terminals (for AC mains power) and output terminals (for DC low voltage power to the LEDs).
- Accessing Terminals: Open the PSU casing to access the screw terminals. This usually involves removing a cover or screws.
- Identifying Terminals:
- AC Input: Look for terminals labeled “L” (Line or Live), “N” (Neutral), and sometimes “G” or a ground symbol (Earth).
- DC Output: Look for terminals labeled “+” and “-” to connect to your LED strips.
- Wire Preparation: Strip a small amount of insulation from the ends of the wires you’ll use to connect to the PSU.
Step 4: Connecting the AC Input to the PSU
This is where you connect the PSU to your mains power. This requires careful attention to detail.
- Live Wire (L): Connect the “Live” wire from your mains power source to the “L” terminal on the PSU. This wire typically carries the hot electrical current.
- Neutral Wire (N): Connect the “Neutral” wire from your mains power source to the “N” terminal on the PSU. This wire completes the electrical circuit.
- Ground Wire (G/Earth): If your PSU has a ground terminal (often a green screw or labeled “G”), connect the ground wire from your mains power source to it. This is a crucial safety feature that protects against electric shock if there’s a fault.
Important Note: The AC wiring must be done in accordance with local electrical codes. Use appropriate gauge wire for the mains voltage. For concealed wiring, consider using properly rated AC cables and junction boxes.
Step 5: Connecting the DC Output to the LED Strip
This is where low voltage LED wiring comes into play, connecting your DC power LED strips to the PSU.
- Positive (+) Connection: Connect the positive (+) wire from the PSU’s DC output to the positive (+) connection point on your LED strip.
- Negative (-) Connection: Connect the negative (-) wire from the PSU’s DC output to the negative (-) connection point on your LED strip.
Methods for Connecting Wires:
- Soldering (Recommended):
- Tin the wire ends and the strip’s connection pads.
- Hold the tinned wire against the tinned pad.
- Apply heat with the soldering iron until the solder flows and creates a strong bond.
- Once cooled, slide a piece of heat shrink tubing over the connection and heat it to create a secure, insulated joint.
- Wire Connectors (e.g., Wago Lever Nuts):
- Strip the wires to the recommended length for the connector.
- Push the stripped wire into the connector’s designated port. Lever-style connectors have levers to secure the wire; push-in connectors require simply pushing the wire in until it clicks.
- Ensure the connection is firm and secure.
Step 6: Testing the Installation
Before closing everything up, it’s time to test your work.
- Double-Check Connections: Visually inspect all your connections to ensure they are secure, correctly polarized (+ to +, – to -), and that there are no stray wire strands that could cause a short circuit.
- Power On: Turn the power back on at the breaker box.
- Observe: Your LED strips should illuminate. If they don’t, or if something seems amiss (flickering, no light), immediately turn the power off and re-check all your connections.
- Using a Multimeter:
- AC Input Voltage: With the PSU connected to mains, set your multimeter to AC voltage and carefully test the voltage between the L and N terminals of the PSU to ensure it’s receiving mains power.
- DC Output Voltage: Set your multimeter to DC voltage. Carefully measure the voltage across the DC output terminals of the PSU. It should match the voltage rating of your LED strips (e.g., 12V or 24V).
- Strip Continuity: You can also use the multimeter in continuity mode to check if there are any shorts between your positive and negative wires before powering up.
Step 7: Securing and Concealing the Wiring
Once you’ve confirmed everything is working correctly, it’s time to tidy up.
- Secure the PSU: Mount the power supply securely in its intended location. Ensure it has adequate ventilation, as PSUs can generate heat. Avoid covering them completely.
- Route Wires Neatly: Use cable clips, zip ties, or conduit to organize and secure all wiring. This not only looks professional but also prevents wires from becoming snagged or damaged.
- Protect Connections: Ensure all connections, especially those made with solder and heat shrink, are well-protected. Use junction boxes if necessary for mains voltage connections.
Advanced Considerations for Hardwired LED Strips
For more complex installations or specific needs, there are additional factors to consider for your permanent LED strip installation.
Dimming Capabilities
If you want to dim your hardwired LED lights, you’ll need a dimmable LED power supply and compatible dimmable LED strips.
- Dimmable PSUs: These often have specific dimming terminals or require specific dimming protocols (like 0-10V or DALI).
- Dimmer Switches: You’ll need a dimmer switch compatible with your chosen dimmable PSU. These are typically wired in-line between the mains power and the PSU, or they might integrate with specific PSU models.
Multiple Strips and Sections
If you’re connecting multiple LED strips or different sections of a long strip, ensure your power supply has enough capacity for the combined load.
- Parallel Connections: Connect multiple strips in parallel to the PSU’s DC output. This ensures each strip receives the correct voltage. Connect all the positive wires of the strips to the PSU’s positive output and all the negative wires to the PSU’s negative output.
- Wire Gauge: For longer runs or higher currents, you may need to use thicker gauge wire (lower gauge number) to minimize voltage drop.
Connecting to Existing Wiring
When connecting LED strips to mains power by tapping into existing home wiring, extreme caution is needed.
- Identify the Correct Circuit: Ensure you are connecting to a circuit that can handle the additional load.
- Use a Junction Box: All connections to existing mains wiring should be made inside a properly rated electrical junction box.
- Professional Help: If you are unsure about how to safely tap into existing wiring, always consult a qualified electrician.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with a good guide, mistakes can happen. Here are some common issues to watch out for during LED strip wiring:
- Incorrect Polarity: Connecting positive to negative or vice versa will prevent the LEDs from lighting up and can potentially damage them. Always verify polarity.
- Underpowered PSU: Using a power supply with insufficient wattage will cause it to overheat, shorten its lifespan, or fail. Always adhere to the 20% buffer rule.
- Voltage Drop: For very long runs of LED strips, the voltage can drop towards the end of the strip, causing the LEDs to appear dimmer. Using thicker wire or a higher voltage strip (like 24V instead of 12V) can help mitigate this.
- Improper Insulation: Exposed wires can lead to short circuits and fire hazards. Ensure all connections are properly insulated with heat shrink tubing or appropriate connectors.
- Overcutting LED Strips: Cutting strips at the wrong points can damage the internal circuitry. Always cut at the designated marks.
- Ignoring Ventilation: Power supplies need airflow to dissipate heat. Blocking the vents on a PSU can lead to overheating and failure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions related to hardwiring LED light strips:
-
Q1: Do I need a special adapter for hardwiring LED strips?
A1: Yes, you need a direct wire LED power supply unit (PSU) or an LED driver designed for hardwiring. These units convert mains AC power to the low DC voltage your LED strips require and have terminals for direct wire connections, unlike standard plug-in adapters. -
Q2: Can I wire LED strips directly to household AC power?
A2: No, you cannot wire LED strips directly to household AC power. LED strips operate on low DC voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V). You must use a power supply unit (PSU) or an LED driver to convert the high AC voltage from your mains to the low DC voltage that the LED strips need. -
Q3: What gauge wire should I use for hardwiring LED strips?
A3: The wire gauge depends on the current (amperage) the strip will draw and the length of the wire run. For most 12V or 24V LED strips drawing up to 5-8 amps over short distances, 18-gauge or 16-gauge wire is typically sufficient. Always check the specifications of your PSU and LED strips, and consult a wire gauge chart if unsure, especially for longer runs to avoid voltage drop. -
Q4: How do I connect multiple LED strips to one power supply?
A4: You connect multiple LED strips in parallel to the power supply’s DC output. Connect all the positive (+) wires from the LED strips to the PSU’s positive (+) terminal, and connect all the negative (-) wires from the LED strips to the PSU’s negative (-) terminal. Ensure the power supply has enough wattage capacity to handle the total load of all connected strips. -
Q5: Is it safe to hardwire LED strips myself?
A5: If you have a good grasp of basic electrical principles, understand safety precautions, and have the correct tools, it can be a safe DIY project. However, if you are at all uncertain or uncomfortable with electrical wiring, especially when dealing with mains voltage, it is always best to hire a qualified electrician to ensure the job is done safely and correctly.
By following these steps and prioritizing safety, you can successfully hardwire your LED light strips for a professional, integrated lighting solution. Remember to always refer to the specific product documentation for your LED strips and power supply for the most accurate guidance.
